Issues and solutions at overseas distribution centers — from the client perspective
Issues and solutions at overseas distribution centers
— from the client perspective

Contents
- (1) Inventory discrepancies occur even with ERP inventory control! Why?
- (2) No more shipping errors! What is the cause?
- (3) What is the risk of warehouse operations becoming over-reliant on key individuals? Standardization is the answer!
- (4) Is there good visibility on overseas warehouse inventories? Cloud-based Warehouse Management System (WMS) is the answer!
- Back to Global Support Top
Has this ever happened in your workplace?


- I use the inventory control function of ERP, but there are too many discrepancies between the stated inventory levels of goods, materials, and raw materials versus the actual quantities in stock.
- We were hoping that ERP would improve the accuracy of inventory, but this has not happened.
Solution

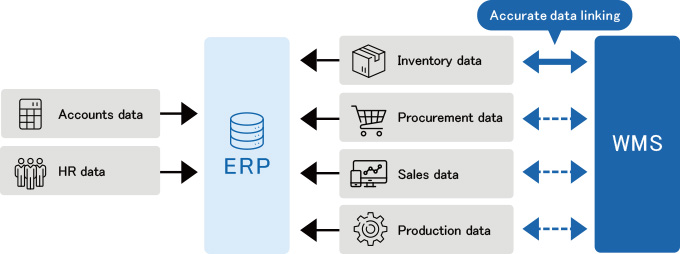
- By gathering accurate information in ERP, information can be centrally managed and utilized. But relying solely on ERP functions for inventory management makes it difficult to gather accurate inventory information, and this approach can actually increase the workload of warehouse workers.
- POINT 1
ERP is most effective when you have first identified the key issues and challenges in the warehouse inventory management, created rules and systems for generating accurate data without increasing workloads, and set up clearly defined job procedures.
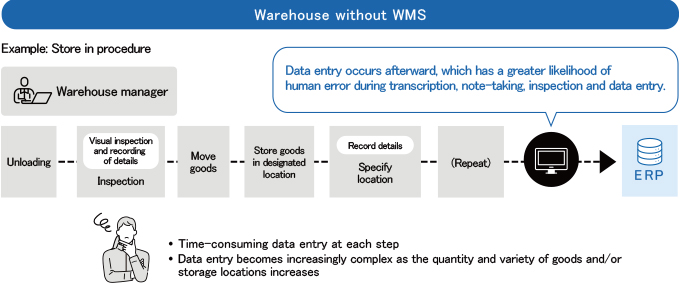
Warehouses that have not embraced IT still rely largely on manual processes such as visual checking and inspection, data entry after the event, and paper dockets. These carry a higher likelihood of minor human errors that can turn into to major problems.
By utilizing Warehouse Management Systems (WMS), complex and processing-intensive warehouse operations can be optimized and streamlined, and inventory accuracy and work precision can be expected to improve.
Benefits
- More accurate inventory
- More accurate operational outcomes
- Reduced labor requirements
- Improved visibility over logistics data
- POINT 2
ERP is a system that is effective only when it consolidates all the information necessary for corporate management and operates it appropriately.
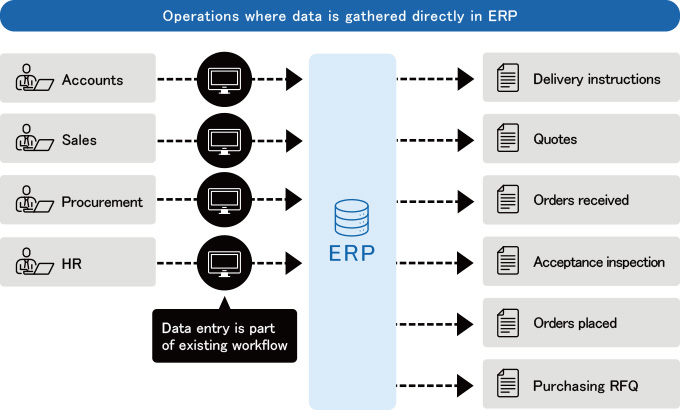
Compared to areas such as accounts, finance, sales, procurement and HR, where data is entered directly in ERP, warehouse operations are based on manual labor, with the associated risk of human error in counting, checking, and data entry processes.
Key differences between warehouse operations and accounts, sales, procurement, and payroll operations
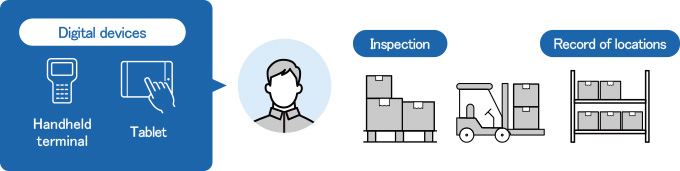
Real-time on-site data entry prevents errors and omissions while reducing workloads. Barcodes and digital devices represent a highly efficient way to obtain data in the field.
Benefits
- Enables real-time in-situ data entry free of errors and omissions
- More accurate inventory management and operational outcomes
- POINT 3
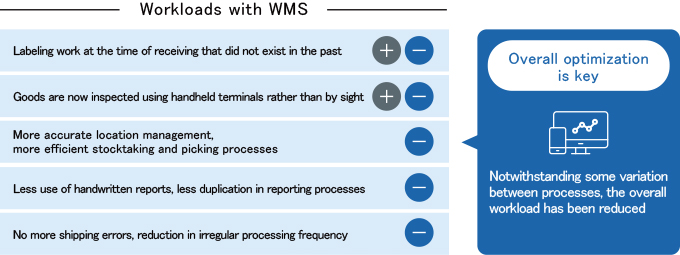
For most processes, WMS effectively reduces workloads and hours worked, and therefore costs. But for some processes, workloads may actually increase. This is primarily associated with WMS features designed to improve operational accuracy.
Overall optimization for more efficient and accurate inventory management involves a balance between the competing demands of improved accuracy and reduced workloads.
Benefits
- Workload can be reduced in some areas without increasing the overall workload
- Greater accuracy in logistics processes
Contents
- (1) Inventory discrepancies occur even with ERP inventory control! Why?
- (2) No more shipping errors! What is the cause?
- (3) What is the risk of warehouse operations becoming over-reliant on key individuals? Standardization is the answer!
- (4) Is there good visibility on overseas warehouse inventories? Cloud-based Warehouse Management System (WMS) is the answer!
- Back to Global Support Top
Contents
- (1) Inventory discrepancies occur even with ERP inventory control! Why?
- (2) No more shipping errors! What is the cause?
- (3) What is the risk of warehouse operations becoming over-reliant on key individuals? Standardization is the answer!
- (4) Is there good visibility on overseas warehouse inventories? Cloud-based Warehouse Management System (WMS) is the answer!